IP address and its class
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a 32-bit number which uniquely identifies the devices like computer, printer, router etc on a TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) network. These devices in a network are termed as host. IP addresses are represented by four numbers separated by dot.
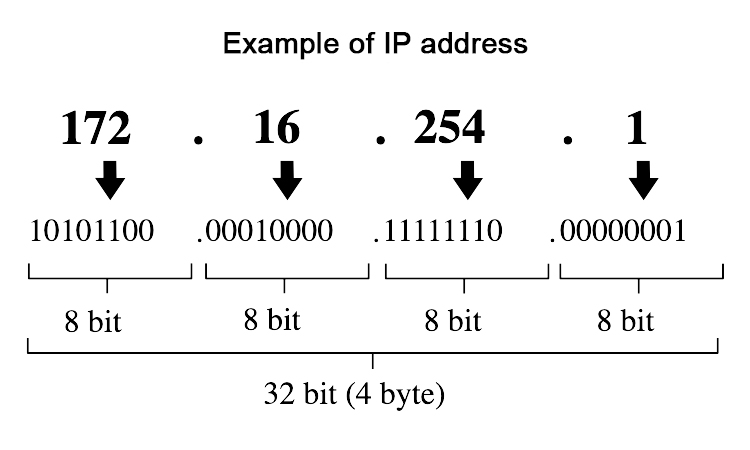
For example, let us consider an IP address 192.168.125.137
The 32-bit notation for above IP address is
1100000010101000111110110001001
For conveniency these 32 bit binary notation is divided into four parts each having 8 bits. Each 8 bits parts are known as octets. The IP address in binary notation is 11000000.10101000.1111101.10001001
Again IP addresses are divided into several classes. Most common are Class A, B and C. Class D and E are not used by end users. Different classes of IP address can simply distinguish by looking at its first octet. All three classes of IP addresses are explained briefly with their range:
Types of IP address
- Class A IP address has their first octet ranging from 0 to 127. Let us consider, an IP address 82.52.36.11. Since its first octet is 82 which is within the range of 0-127, we can say it is a class A IP address. Its default subnet mask is 255.0.0.0
- Class B IP address has their first octet ranging from 128 to 191. Let us consider, an IP address 182.36.52.11. Since its first octet is 182 which is within the range of 128-191, we can say it is a class B IP address. Its default subnet mask is 255.255.0.0
- Class C IP address has their first octet ranging from 192 to 223. Let us consider, an IP address 192.136.42.11. Since its first octet is 192 which is within the range of 192-223, we can say it is a class C IP address. Its default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0