SEE Class 10 computer science new curriculum and syllabus
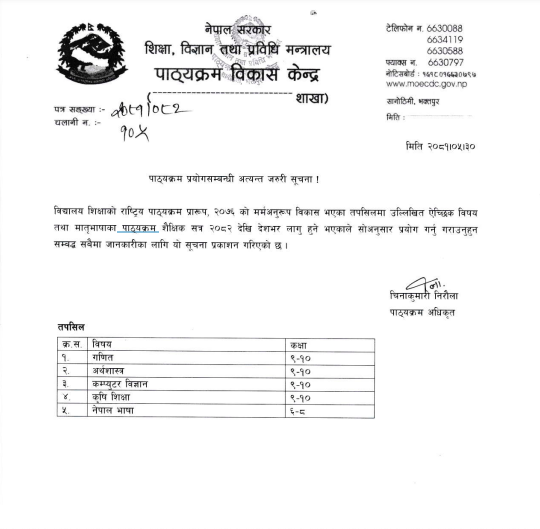
Curriculum Development Centre (CDC Nepal) has changed the syllabus of class 10 computer science and has included python programming language instead of QBASIC. Following is the official notice of CDC Nepal.
Computer Science new curriculum chapters
- Computer Network and Communication
- Database Management System
- Multimedia
- Programming in Python
- AI and Contemporary Technologies
Course content of New Curriculum
| S.N. | Chapter | Chapter Content | Hour (Th + Pr) |
| 1. | Computer Network and Communication | 1.1 Concept of telecommunication and key terminology: Definition, Broadband, Bandwidth, Throughput, 3G/4G/5G, Data Packets, Frequency 1.2 Communication channel/Media: Wired (CAT6, Optical Fiber), Wireless (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, RFID, satellites) 1.3 Connector: RJ45, Media Convertor 1.4 Networking Devices: Repeater, Hub, Switch, Bridge, and Router 1.5 Topologies overview: BUS, Star, Ring, Hybrid 1.6 Overview of different Network based on coverage: PAN, LAN, MAN, WAN 1.7 Network Architecture: client-Server, Peer to peer 1.8 Concept of IP addressing (IPv4 and IPv6) 1.9 Concept of internet, intranet and extranet Practical Task a) Demonstrate and identify devices and cables b) Check IP address, and default Gateway. c) Demonstrate the use of following command: ping, ipconfig, tracert, nslookup d) Demonstrate RJ45 and Fiber connectors. |
14+6 |
| 2. | Database Management System | 2.1 Definition, importance and application of database 2.2 Data, Information, Database, DBMS 2.5 Keys: Primary Key, Foreign Key Practical Task a) Download and Install open source database application such as MySQL b) Create a database. c) Create tables which include various attributes with appropriate data types. d) Implement Primary key in tables. e) Define relationships between tables using foreign keys. f) Modify table using alter command g) Insert appropriate data in tables. h) Display all the data using the select statement. i) Display specified record using where clause and like (%, _) j) Update and delete the records from the existing tables | 10+16 |
| 3. | Multimedia | 3.1 Concept of Multimedia Technology 3.2 Multimedia Component Concepts (Text, Graphics, Audio, Video, Animation) 3.3 Graphics: Concept of Raster and Vector, Graphics File Formats (PNG, GIF, JPG, SVG, PDF) 3.4 Audio: Concept of Audio Waveform, Audio File Formats (MP3, AAC, WAV) 3.5 Video: Concept of Frame rate and Resolution (SD, HD), Video File Formats (MP4, MOV, AVI) 3.6 Animation Concept: 2D and 3D animation Practical Task a) Create and edit in graphics using tools such as Pixlr X or Adobe Photoshop and work with following: Layers, Text, Shapes, Image Placement, Selection, Exporting b) Create and edit in audio using tools such as Audio mass or Audacity and work with following: Recording, Importing, Cutting, Effects, Exporting c) Create and edit in video using tools such as Clip champ or CapCut and work with following: Importing, Timeline, Cutting, Transition, Effects, Text, Exporting. Project Work a) Students work on creating, editing, and finalising an image, audio, or video file using the basic features of image, audio, or video editing tools that are available or accessible in your computer lab. Demonstrate in class what they produce. | 10+12 |
| 4. | Programming in Python | 4.1 Revision of the basics of Python return type, passing 4.3.1 Importing and use of standard libraries 4.3.2 Introduction to popular libraries (eg. Math, random, Pandas, Turtle, matplotlib) 4.4 Graphics Using Turtle: Define, draw turtle, function (Forward, Backward, Left, Right, Penup, color, Fillcolor), shape 4.5 Error handling: errors and exceptions, try-except blocks 4.6 File handling using panda library 4.6.1 Concept of File Handling in python 4.6.2 Concept of mode of File Handling (Read, Write, and append a File) 4.6.3 Read and write CSV file using standard library (eg. Panda) 4.7 Introduction to data visualization using any suitable package (eg. Matplotlib, plotly or GGPlot): Line chart, pie plot, and bar graph Practical Task a) Demonstrate the structure of user defined functions. b) Install and use of packages and libraries (e.g. Pandas, Turtle, matplotlib). c) Draw various shapes (circle, rectangle, polygons etc) and fill the colors using turtle. d) Demonstrate the read and write in CSV file using concept of file handling using panda packages. e) Draw and plot bar, line, pie using data visualization tools using matplotlib package Project Work (use any python platform, eg: pycharm, Jupyter notebook or google Colab) a) Develop a simple project of your own using libraries, user defined functions and visualization tool. b) Prepare a simple report covering outlining the process you followed during the development time. | 16+18 |
| 5. | AI and Contemporary Technologies | 5.1 Concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) 5.2 Concept of learning techniques in machine (supervised and unsupervised) 5.3 Concept of AI in robotics, simulation of simple robotic tasks 5.4 Definition of Generative AI (Such as Copilot, ChatGPT, Gemini) 5.5 Application of integrated AI tools such as google doc and email, office 365. 5.6 Ethics in AI: Bias, Privacy, and Security 5.7 Concept of Internet of Thing (IoT) and its applications 5.8 Concept of Virtual and Extended Reality (XR) Education Practical Task a) Demo on AI based robotics simulations b) Apply the use of generative AI tools such as ChatGPT, Copilot, Geminin in through learning process. c) Surf e-com, e-gov, e-education sites. d) Surf virtual tour sites and XR practices. | 14+12 |
Note: Total of 64 hours of teaching is for each theory and practical